Mustelus Punctulatus
– Blackspotted Smooth-Hound –

| Conservation status |
|---|
 Data Deficient (IUCN 3.1) |
| Scientific classification |
Mustelus punctulatus A. Risso, 1827
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Order: | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family: | Triakidae |
| Genus: | Mustelus |
| Species: | M. punctulatus |
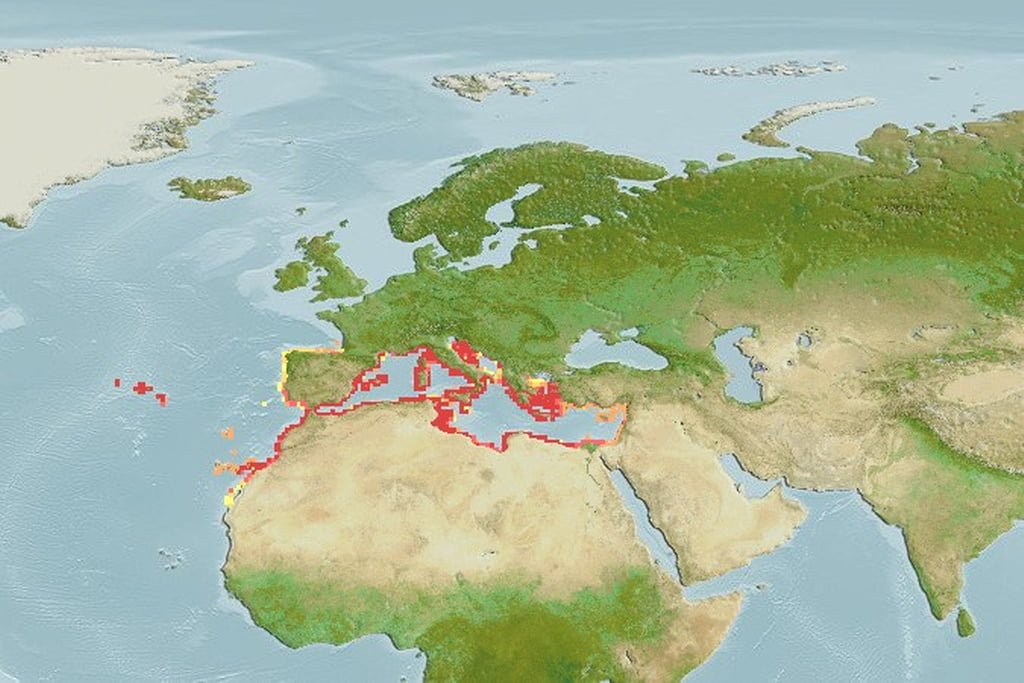

The blackspotted smooth-hound (Mustelus punctulatus) is a houndshark of the family Triakidae found on the continental shelves of the subtropical eastern Atlantic from the Mediterranean to the Western Sahara, between latitudes 45 and 20°N, from the surface to a depth of 250 m. It can reach of a length of 1.5 m.
Mediterranean Shark [1] ( Mustelus punctulatus ) – a little-studied type of cartilaginous fishes kind of ordinary marten sharks family marten sharks detachment carcharhiniformes . It lives in the northeastern and central-eastern parts of the Atlantic Ocean . Probably reproduces by live birth . The maximum recorded length is 95 cm. It does not pose a danger to humans. Has no commercial value.
Description
European weasel sharks have a short head and an elongated body. The distance from the tip of the muzzle to the base of the pectoral fins ranges from 17% to 20% of the total body length. The muzzle is slightly elongated and blunt. Oval large eyes are extended horizontally. Spiracles are located behind the eyes. There are labial grooves in the corners of the mouth. The upper furrows are longer than the lower ones. The short mouth is equal in length to the eye and accounts for 2–3.1% of the body length. Blunt and flat teethasymmetrical, with a small central point, lateral teeth are present only in very young sharks. The cheek-pharyngeal teeth cover the tip of the tongue and the anterior third of the pharynx. Distance between dorsal fins is 18-22% of body length. The pectoral fins are small, the length of the anterior margin is 12-14%, and the posterior margin is 7.2-11% of the total length, respectively. The length of the anterior margin of the pelvic fins is 7.4–8.8% of the total body length. Anal fin height 2.3-3.4% of total length. The first dorsal fin is larger than the second dorsal fin. Its base is located between the bases of the pectoral and pelvic fins. The base of the second dorsal fin begins in front of the base of the anal fin. The anal fin is smaller than both dorsal fins. There is a ventral notch at the edge of the upper lobe of the caudal fin.The caudal fin is almost horizontal. The color is gray or gray-brown with dark spots. The belly is light [5] [6] .
Distribuition
European marten sharks live in the central western and southwestern Atlantic in the Mediterranean Sea and off the coast of Western Sahara . They are found on the continental shelf at a depth of 200 m [4] .
Taxonomy
The species was first scientifically described in 1827 [2] . Mediterranean sharks are often confused with stellate and European mustelids, whose ranges overlap [3] .
Biology
Mediterranean mustelids sharks are likely to breed by live birth. Males and females reach sexual maturity at 50–55 cm and 60 cm lengths, respectively. The length of newborns is about 31 cm. The diet consists mainly of benthic crustaceans [5] [7] .
Alimentation
The dogfish feeds mainly on crustaceans, cephalopods and herring.
Dimensions
Although they can grow up to 2m, their usual maximum size is 1m and 50cm. They commonly grow to 1m – 1m and 20cm with a birth length of about 35cm. One of the largest specimens ever recorded in the Mediterranean is a 1 m and 65 cm pregnant female with 17 embryos captured in the Adriatic on March 15, 2000.
Reproduction
It is viviparous, although a primitive placenta develops in pregnant females. The litters are 4-15 young (usually 10) and the gestation is 10-11 months. Females mature to around 80cm, males between 70 and 74cm.
Human Interaction
The species is not dangerous to humans. It ends up in commercial fishing nets as a by- catch . Probably, in the Mediterranean Sea region, the meat of these sharks is used for food. There are insufficient data to assess the conservation status of the species [3] .
Dangers
It is caught by trawling and used for human food, to obtain fish oil and to make animal feed.
Parasites
As other sharks, the blackspotted smooth-hound harbours a number of parasites. Triloculotrema euzeti is a monocotylid monogenean parasite within the nasal tissues, which was described in 2016 from sharks caught off Tunisia.[1]