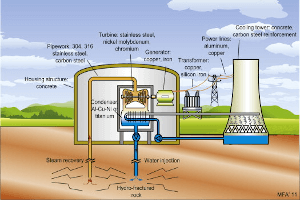
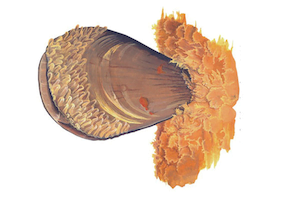
Spisula Solida
– Surf Clam –

| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Bivalvia |
| Subclass: | Heterodonta |
| Order: | Venerida |
| Superfamily: | Mactroidea |
| Family: | Mactridae |
| Genus: | Spisula |
| Species: | S. solida |
| Binomial name |
|---|
| Spisula solida (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Description
The shell of this bivalve is thick and robust, its triangular shape and its angles are rounded; it measures between 2.5 and 3.5 cm but can reach 5 cm in width. The valves, symmetrical, are convex , with more or less marked concentric growth streaks. The hinge has two finely crenellated V-shaped cardinal teeth and two lamella-shaped lateral teeth. From ivory white to cream , the shell is covered with a thin cuticle brownish or periostracum * especially present to the ventral edge. The interior of the valves is white; the palleal sinus * is deep.
Biotope
Shallow burrower, this surfclam is found on fine sandy beaches or shellfish from the first meters up to about 50 m deep. One would have noted its presence up to 160 m of depth in its southern zone of distribution. It prefers areas with strong current where food is abundant.
Similar Species
Spisula ovalis : more elongated shell shape. Some authors put Spisula ovalis (J. Sowerby, 1817) in synonymy with S. solida .
Mactra stultorum : larger and significantly more fragile shell, smooth cardinal teeth.
Food
A suspensivorous filter *, the surf clam feeds on the fine food particles of phytoplankton * (diatoms, microscopic algae) that it captures on the surface of the sediment.
Reproduction
The sexes are separated and fertilization takes place in open water. There is no sexual dimorphism * and only the color of the gonads can differentiate the male from the female.
The laying takes place all year round depending on the water temperature with a peak in summer.
The larva *, which comes from the egg, has a fairly long pelagic * life, of the order of 3 to 4 weeks. Growth is quite rapid since the maturity of the spisula is reached between 18 months and two years.
Its lifespan is estimated at around ten years.
Associated Life
It is a favorite prey of certain predators such as the natice Euspira catena or the starfish Asterias rubens which live in the same ecosystem *.
Various Biology
Depending on the biomass *, it forms schools of varying density, often greater than 200 individuals per m².
Further Information
This edible species, with little esteemed flesh, can be dredged with small units (less than 11 m) for professionals; with a fork, a toothed claw or a rake for recreational fishermen during high spring tides.
It will be noted that the empty shells tend to take on a blue, brown or blackish color after a prolonged stay in the sand or the mud.