Bothus Podas
– Wide-Eyed Flounder –


| Conservation status |
|---|
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] |
| Scientific classification |
Bothus podas (Delaroche, 1809)
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Pleuronectiformes |
| Family: | Bothidae |
| Genus: | Bothus |
| Species: | B. podas |
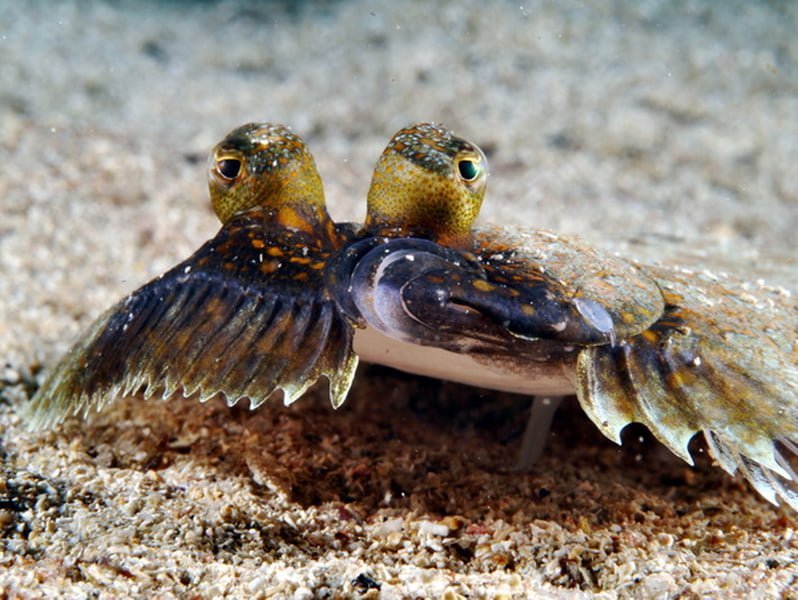
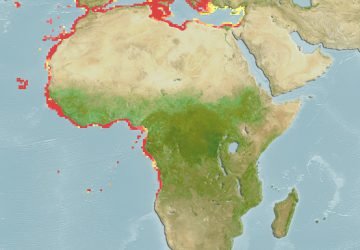

Bothus podas, also known as the wide-eyed flounder, is a flounder in the genus Bothus, native to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Coast of Africa.
During the reproductive season, males court and mate successively with females in their territories, and females seem to show mating fidelity to their dominant male. Data also show that courtship plays an important role in determining male success in mating.[3]
The turbot ( Bothus podas Delaroche , 1809 ) is a sea fish of the Bothidae family .
Description
It has the typical flattened appearance of flatfish with both eyes on the left side of the body which is very wide. The lateral line has a double curve in its most anterior part. The mouth is small and carried on a short protruding snout; the mandible is longer than the maxilla . There is an evident sexual dimorphism : the male has very distant eyes and a flat front profile. Even in the female, however, the eyes are not close.
The livery can be sand-colored with irregular and shaded dark spots or darker with dark ocellated spots with a clear center, well defined. The latter coloring is more frequent in males.
It can reach a length of 40 cm but usually does not exceed 20 cm.
Distribution and Habitat
It is a widespread species throughout the Mediterranean Sea and in the eastern Atlantic Ocean between the Strait of Gibraltar and Angola . In the Italian seas it is common everywhere.
It populates bottoms of fine sand between 2 and 400 meters deep and is frequently encountered in very shallow waters.
Alimentation
It feeds on benthic invertebrates and small fish.
Reproduction
It reproduces in spring-summer; eggs and larvae are pelagic . The right eye migrates to a length of about 3 cm, when the larva has red spots at the base of the dorsal and anal fins .
Fishing
It captures in quantities with bottom trawls and gill . It also bites very easily to any animal bait but has no value due to its small size. The meats are still good, especially if fried or in soup.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia