Scientific classification
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Angiosperms |
| Class: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Senecioneae |
| Genus: | Jacobaea |
| Species: | J. maritima |
Binomial name
Jacobaea maritima
(L.) Pelser & Meijden
Synonyms
Othonna maritima L. (basionym)Cineraria maritima (L.) L.Senecio maritimus (L.) Rchb. [non L.f.]Maritima bicolor Willd.Senecio bicolor (Willd.) Tod. [non Viv.]Senecio cineraria DC.Cineraria gibbosa Guss.Cineraria nebrodensis Guss.Cineraria ambigua Biv.Senecio bicolor subsp. cineraria (DC.) ChaterSenecio cineraria subsp. bicolor (Willd.) Arcang.[1][2][3]
Jacobaea maritima, commonly known as silver ragwort, (formerly known as Senecio cineraria) is a perennial plant species in the genus Jacobaea in the family Asteraceae, native to the Mediterranean region. It was formerly placed in the genus Senecio, and is still widely referred to as Senecio cineraria; see the list of synonyms (right) for other names.
It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant for its white, felt-like tomentose leaves; in horticultural use, it is also sometimes called dusty miller, a name shared with several other plants that also have silvery tomentose leaves; the two most often to share the name are Centaurea cineraria and Lychnis coronaria.
Description
Silver Ragwort is a very white–wooly, heat and drought tolerant evergreen subshrub growing to 0.5–1 m (1.6–3.3 ft) tall. The stems are stiff and woody at the base, densely branched, and covered in long, matted grey-white to white hairs. The leaves are pinnate or pinnatifid, 5–15 centimetres (2.0–5.9 in) long and 3–7 centimetres (1.2–2.8 in) broad, stiff, with oblong and obtuse segments, and like the stems, covered with long, thinly to thickly matted with grey-white to white hairs; the lower leaves are petiolate and more deeply lobed, the upper leaves sessile and less lobed.
The tomentum is thickest on the underside of the leaves, and can become worn off on the upper side, leaving the top surface glabrous with age. The flowers are yellow, daisy-like in dense capitula 12–15 millimetres (0.47–0.59 in) diameter, with central disc florets surrounded by a ring of 10–13 ray florets, and enclosed in a common whorl of bracts at the base of the capitulum. The seeds are cylindrical achenes.[4][5][6]
Distribution
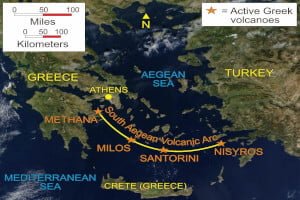
Jacobaea maritima is native to the western and central Mediterranean region, in northwest Africa (Morocco, northern Algeria, Tunisia), southern Europe (Spain, Gibraltar, southern France including Corsica, Italy including Sardinia and Sicily, Malta, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, Serbia, Macedonia, and Greece), and the far west of Asia (Turkey). It occurs primarily on cliffs and rocky coastal sites, more rarely inland.[2][3][5]
It is also naturalised further north in Europe (north to Great Britain and Ireland, where occurring mainly in mild coastal areas[4][5]) and locally in North America.[7]
Ecology
As with many other densely tomentose plants, the tomentum on the leaves is used by some species of bees (e.g. Anthidium manicatum and Anthidium oblongatum in Megachilidae) for nest-building.[8]
Hybrids are known with Jacobaea erucifolia and Jacobaea vulgaris; the hybrid with J. vulgaris is fertile, producing a wide range of intermediate progeny.[4][5]
Cultivation and uses
J. maritima ‘Silverdust’, a cultivar selected for its dense silvery tomentum.
Jacobaea maritima is widely used in horticulture for its silvery foliage. It is winter-hardy in USDA Zones 8-10, tolerating winter temperatures down to -12° to -15 °C,[6][9] tolerant of light shade but preferring full sun.[6] In colder areas it is grown as an annual plant. Many cultivars have been selected for particularly dense silvery tomentum, such as ‘Cirrus’, ‘New Look’, ‘Ramparts’, ‘Silverdust’, ‘Silver Filigree’, and ‘White Diamond’.[6] It has been recommended in North America for its fire resistance[10] resistance to browsing by deer,[11] and its salt tolerance.[12]
The cultivar ‘Silver Dust’ has gained the Royal Horticultural Society‘s Award of Garden Merit.[13]
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia