With advance research and studies, we came up with renewable energy sources that could work in the same way as fossil fuels work and would be safer to use. They wouldn’t harm the environment much and will in abundance for us to use. Hydropower, solar power, wind energy, and geothermal energy are some sources that work great for our needs.
What is geothermal energy and is it renewable?
Geothermal energy is formed by the molten and heated interiors of the earth, which are positioned at the planet’s core. The molten materials have a very high temperature and can provide a large amount of energy for various purposes.
Like any other renewable source of energy, geothermal energy is extracted from the earth itself through machinery. Geothermal energy is present in the core of the earth in the form of heat and is extracted by us to work as a fuel for various purposes. This heat present inside the earth is not produced by the Sun. It is a renewable source of energy as its almost unlimited amount of heat present in the earth’s core. We would be able to utilize a lot of this source for a long time as the heat present inside the planet would last for a long time to come.
What is the source of geothermal energy and what type of energy is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy, as has been mentioned above, comes from the inside of the earth. This energy is produced in the earth’s core due to the molten interiors. The heat generated by these molten rocks and fluids provides the needed energy which can be harnessed to pump electricity, etc. The earth’s interior consists of radioactive materials which sometimes go through fission or radioactive decay and create a healing effect on the surroundings. This leads to the creation of some hot spots that give rise to geothermal energy.
Geothermal energy is present in an abundant amount in the earth’s core. Due to this fact, it is a renewable source of energy that can be used in large amounts. This makes sure that it has a bright future and would be used for various purposes for many generations to come.
What is geothermal energy used for?
There are various vital uses of geothermal energy that are not very popular, but one should know about it.
Generation of electricity:
For this process to work, massive turbines and generators are used that connect to pumps and bring out the energy present inside the earth. The heat energy from down below is used to convert water into steam. The purpose of the steam is to move turbines, which ultimately produce high amounts of electricity. This process is environmentally friendly and is not very difficult to execute.
A good read for you: Everything You Need to Know About Biomass Energy
Heat cold buildings:
During extreme winter months, to heat the inner temperature of a house or a building, instead of using a central heating system, geothermal energy is used. Pipelines are connected to the bigger pipelines that are ultimately connected to the hot spots that are made inside the earth’s crust. Due to this, the heat gets transferred to the buildings and brings up the temperature ultimately.
Read next: 4 Renewable Forms of Energy to Use in Your Home
The energy inside the molten earth can be used to power generators and pumps that work on a large scale. The molten core of the planet is a storage of energy that can be used to heat cool buildings if need be.
Daily chores:
Geothermal energy acts as the best replacement for geysers and electrical water heaters. They can be used to heat water at little cost in the long run. This water can be used for daily chores such as bathing, washing, cooking, etc.
What is the cost of geothermal energy?
Considering the amount of money we spend on non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels, generating geothermal power doesn’t cost a lot, especially in the long run. An entire power plant has to be built that would have all the required machinery to generate geothermal power. An average power plant costs about $0.01-$0.03 every KWH. This cost can vary according to the type of geysers and the time when it is being produced.
To estimate costs in such cases depends on the time when the energy is generated. For instance, when geothermal energy is in demand, like in winter months, the generation could be costly. In the season of low demand, the production of geothermal energy could be more profitable.
What is good about geothermal energy?
There are various advantages of using geothermal energy instead of going for fossil fuels.
Abundance:
To start with, this type of energy is present in abundance in the earth’s core and is a renewable form of energy. It can be produced anywhere on earth. You just have to build a power plant over any hotspots inside the earth’s crust, and you would be able to extract a lot of energy under a short while.
Promised profits:
With fossil fuels depleting in quantity, people have no option but to switch to renewable energy sources such as geothermal energy. As soon as more methods of generating and using this energy will come up, its requirement would increase and would bring you a lot of profit for sure.
Various uses:
Geothermal energy has several purposes. From industrial applications like electricity generation to heating water for household uses, geothermal energy comes as a handy source of energy.
What is a disadvantage of geothermal energy?
Like any other energy source, renewable or non-renewable, geothermal energy has various geothermal energy pros and cons.
Harmful emissions:
When geothermal energy is generated, the emissions that are produced during the production get mixed with the atmosphere by traveling to the surface and then to the atmosphere. This impacts the environment and sometimes creates problems like being hard to breathe.FREE ebook!
All You Need to Know about Residential Solar Panels-Buyer’s Guide
Earth instability:
Power plants that used to generate geothermal energy are enormous. The construction of such power plants can cause land deformation and can affect land stability as well, which may erode the soil and make the ground nearby weak and unrested.
What type of energy is geothermal? What percentage of geothermal energy does the U.S. use?
Geothermal energy is in abundance inside the earth’s crust. This abundance of heat energy makes it a renewable and sustainable form of energy. This energy is often best used as power for various power plants and to provide heat to large structures.
Out of all the geothermal energy produced in the United States, only 0.4% of it is used in the production of electricity. With the efficient use and production of this renewable energy, costs can be saved, and fossil fuels can be conserved.
The future of geothermal energy?
With geothermal energy present in so much abundance inside the earth, this can be a beneficial source of energy for future generations. It doesn’t harm the environment as much as other forms of energy generation and is reliable as well. Like all the other renewable resources such as hydro, solar, and wind, geothermal energy has a very bright future. It is considered to be a critical source of power and would be used in more efficient ways in the future due to advanced and cheaper technology. Scientists are working on more ways through which this source of energy can be and make our lives even more comfortable.
History of geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is no new concept on our planet. According to history, geothermal energy was first used about 10,000 years ago by Paleo-Indians in North American. They had discovered some sources of this energy, such as Hot springs and natural geysers. They started using them to go through various daily chores such as bathing, washing, cooking, etc. The next use of heat energy from the inside of the earth occurred in Italy.
Example of geothermal energy
Many examples can be found on the face of the earth for geothermal energy. There are some wonders of nature that work on the scorching temperature in the coldest of the weather. Hot springs are one of the biggest of these wonders. They are usually found in cold climates such as Iceland, Alaska, etc. Hot spring can be a natural example of geothermal energy. They have been in use for over 10,000 years. Paleo-Indians used to make use of these sources for various purposes, such as cooking, bathing, and washing.
How is geothermal energy generated and related questions
Power plants of massive sizes are used to generate geothermal energy. They can be placed anywhere around the world as the hot spots created by the earth’s interiors are created almost everywhere. All that is required is connecting the power plants to the inside of the earth’s crust so that energy flow is uninterrupted. The heat rising from the inside of the earth would be used to convert the water kept into steam. This steam will increase further and in high amounts and give power to turbines to move. This movement of the turbines will generate the required electricity.
You would love to read also: A Complete Guide On Geothermal Power Plants
Hotspots of geothermal energy inside the earth act as reservoirs for power, and they can be used to generate electricity whenever need be.
What is an example of geothermal energy?
A natural and working example of geothermal energy is hot springs that have been used for more than 10,000 years for cooking, bathing, and cleaning purposes.
What is the energy source of geothermal energy?
The radioactive elements present deep inside the earth’s core form, the energy source of geothermal energy. They produce heat in large amounts and create hot spots.
What is the cost of using geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy can be used on an average cost of $0.01 to $0.03 every Kilowatt Hour. This cost highly depends on the type of geothermal heat pump being used and the time of year.
What about geothermal energy for homes?
Tunnels are dug to bring geothermal energy to homes, which can be used to heat the house during cold weather.
What is geothermal energy for kids?
Geothermal energy is an alternative energy source that can be used for various purposes, such as bathing, cooking, and cleaning. This energy is produced from the inside the earth.
What is geothermal energy? How is it used?
Geothermal energy is produced from the molten materials present inside the earth. It is used to create electricity and heat buildings during cold weather.
What is the ultimate source of geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is produced by the heat emitted by the molten materials present in the core of the earth.
What is geothermal energy? What are its advantages and disadvantages?
The energy produced from the core of the earth is geothermal energy.
The advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy are that it is a renewable form of energy, but it emits harmful gases to the atmosphere.
Final words
With geothermal energy getting popular day by day, it is essential to know more about this source of energy. For efficient execution of our daily chores, using such energy sources could prove beneficial in the long run, even on an individual level. Moreover, going for such an option is going to help save the environment and conserve non-renewable sources for future generations as well.

Everything You Need to Know about Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is a fascinating sustainable energy resource that we have successfully taped into.
Humankind tapped into the huge growth potential of energy, for the first time, during the Western industrial revolution of the 18th to 19th century. Fossil fuels – coal in particular – were used to power ever-developing engines and, later, to generate electricity. Fast-forward to the mid-20th century. Despite the innumerable benefits of fossil fuels, their environmental impact started being felt.

It was only in the late 20th century when the energy crises of 1973 and 1979 proved the extent to which humanity had become reliant on fossil fuels, that the environmental movement reached global scale. In the 21st century, humanity would finally find a cleaner alternative: renewable energy (e.g. solar energy, wind power, geothermal energy, biomass and hydro power).
Energy security has become a mandatory criterion for the assessment of a country’s sustainability. In light of concerns regarding climate change, wastes and the security of future generations we have been tasked with finding energy resources that can supply the world’s expanding needs (without harming the environment). One such resource is geothermal energy.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
- Geothermal Energy Definition
- Brief History of Geothermal Power
- Frequently Asked Questions About Geothermal Power:
- What is Geothermal Power?
- Is Geothermal Energy Renewable or Nonrenewable?
- Why is Geothermal Energy Considered a Renewable Resource?
- What is the Source of Geothermal Energy?
- How is Geothermal Energy Produced?
- How is Geothermal Energy Used?
- What is the Environmental Impact of Geothermal Energy?
- Geothermal Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
- Cost of Geothermal Power
- Interesting Geothermal Power Facts
- Examples of Geothermal Energy (outlining the importance of G.E.)
- The Future of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal Energy Definition
In order to define geothermal energy, we must look to the past. Geothermal Power has been around for as long as the Earth has existed. Our forefathers may not have used it under the form of advanced air conditioning systems or power plants, but they did use it for bathing and cooking. The word ‘geothermal’ traces its roots to the Greek words “geo” (earth) and “therme” (heat).
“Geothermal Power is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter.”
Definition of Geothermal Power, according to Wikipedia.
For more details about what geothermal energy is and how it works, read our full story here.
Brief History of Geothermal Energy

Geothermal resources have been around since the dawn of mankind. History tells us that geothermal energy was first used over 10.000 years ago by the Romans, American Paleo-Indians, and Chinese peoples, for heating, cooking, and bathing. However, the industrial use of Geothermal Power can be traced back to the late 18th century.
The first documented attempt of using geothermal energy to produce electricity was initiated by a group of Italians. They managed to successfully build an electric generator, powered by steam erupting from the Earth, at the Larderello fields in 1904. (Larderello is still producing today).

Exactly 18 years later, the United States would also attempt to develop geothermal power at “The Geysers” steam field of Northern California. Sadly, the project failed because the pipes of that time were not strong enough to withstand the corrosion and abrasion of impure particles.
Many individuals attempted to heat their own homes using geothermal energy, but Prince Piero Ginori Conti was the first to harness this power. He successfully created a prototype generator that could deliver enough wattage to light 4 light bulbs. His prototype became the brain child project that encouraged the serious exploration of Geothermal Power production.

In 1960, Pacific Gas and Electronic began work on the first large-scale geothermal power plant in San Francisco. It could produce 11 megawatts of energy. Fast-forward to the 1973’s, when the oil crisis forced many countries to start looking for alternative energy sources. In the 1980s, geothermal heat pumps (GHP) had already become a popular solution because they reduced cooling & heating costs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Geothermal Energy
Because geothermal energy is a relatively new industry, most people have a lot of questions about it. “How does geothermal energy work?”, “How is geothermal energy used?” etc. We will try to answer all of these questions in this section.
1. What is Geothermal Energy?
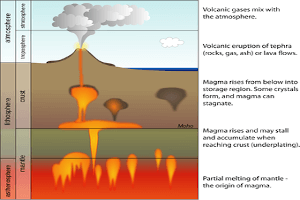
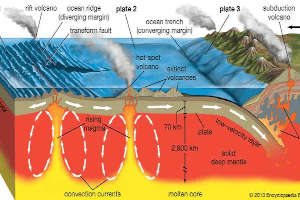
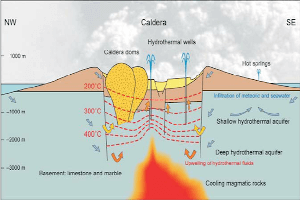
In simple terms, Geothermal Power is energy that comes from the heat within the Earth. The Earth’s double-layered core (extremely hot molten iron surrounding a solid iron center), can be found 4,000 miles beneath the surface. Science says that the core’s temperature varies between 5,000 and 11,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Due to the continuous (and slow) decay of radioactive particles, the Earth produces heat. As you can imagine, excess heat and magma must be released somehow. This is where the Earth’s mantle comes into play.

The mantle surrounds the Earth’s core in 1,800 miles of rock and magma. However, the Earth’s uttermost layer isn’t continuous. It is broken into smaller pieces called plates, which form ocean floors and continents. These plates are also constantly moving at a rate of approximately one inch per year (continental drift). Through this movement, continental plates drift apart or collide (resulting in earthquakes). In the areas where the crust is fractured, thinned or faulted, hot magma comes close to the surface. Magma that comes in direct contact with water represents Geothermal Power.
2. Is Geothermal Energy Renewable or Nonrenewable?
Geothermal energy is renewable. This means that it never runs out. Even for areas that are reliant on a reservoir of hot water, the volume taken out to produce Geothermal Power can be reinjected, thus making it an energy efficient and sustainable resource.
3. Why is Geothermal Energy Considered a Renewable Resource?
Geothermal energy is considered a renewable resource because it uses the Earth’s heat that is constantly produced beneath the surface, and water that is replenished by rainfall.
4. What is the Source of Geothermal Energy?
Many people ask: “Where does geothermal energy come from?” The immediate response would be ‘from the Earth’. Our planet is a hotbed of Geothermal Power. But this doesn’t mean that geothermal energy is always visible, or that it always comes in contact with the Earth’s surface. Apart from several visible features of Geothermal Power, including hot springs, fumaroles, geysers, and volcanoes, most geothermal energy cannot be seen.

Sometimes there are no clues of geothermal energy because it is hidden well underground. In order to find the source of Geothermal Power, geologists must study geological maps or aerial photographs, analyze the concentration of metals in the soil and research the chemistry of water.
5. How is Geothermal Energy Produced?
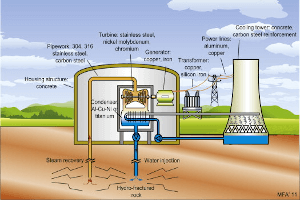
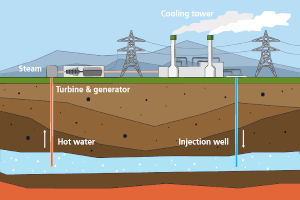
As previously mentioned, geothermal energy is produced when the Earth’s core heats the water on the surface. Sometimes, when people ask “How is geothermal energy produced?” they are referring to how electricity can be obtained from Geothermal Power. Geothermal power plants are used to transform steam and hot water into electricity.
How Geothermal Power Plants Work
Unlike other renewable energy sources (e.g. wind power, solar power), geothermal energy is a baseload power source. This means that the power output of a geothermal plant remains consistent 24/7, making it more reliable.
Traditional power plants use steam to rotate a turbine, which activates a generator. The generator then produces electricity. However, most power plants use fossil fuels to turn water into steam. Geothermal power plants use steam directly from the Earth’s surface. In order to bring Geothermal Power to the surface wells must be drilled into the surface of the earth.
At present, there are three types of geothermal power plants:

- Binary cycle power plants. These plants operate with lower water temperatures (approx. 225-360 degrees Fahrenheit). Heat from the water is used to boil a working fluid –generally an organic compound with a low boiling point- that vaporizes in a heat exchanger and used to power the turbine. Once the cycle is completed, the water is reinjected into the ground, where it is reheated by the Earth. Because the working fluid and water are stored separately the binary cycle power plant has little to no air emissions.

- Flash steam power plants. These are the most common types of geothermal power plants that use extremely hot water (over 360 degrees Fahrenheit). The water flows through underground wells and pipes under its own pressure. As it starts flowing upwards, the water loses pressure and turns into steam that turns the turbine. Once the process is complete, condensed steam and leftover water is reinjected into the reservoir.

- Dry steam power plants pipe steam directly from underground. The steam flows upwards, through pipes, and powers turbines. At present, there are only two known underground sources of steam in the US (Yellowstone National Park’s ‘Old Faithful’ geyser and ‘The Geysers,’ in Northern California).
Now that you know how geothermal energy works in the production of electricity, you are probably wondering: “what is geothermal energy used for?” Let’s find out!
6. How is Geothermal Energy Used?
Geothermal Power is sitting underneath the Earth’s surface. All we have to do is to tap into this incredible resource. Geothermal energy can be used in three ways:
- Geothermal power plant. Steam and hot water from the Earth’s surface can be piped with the help of underground wells and used to generate electricity in a special power plant.
- Geothermal heat pump. At a few feet below the ground, water temperatures average between 50 and 60 degrees Fahrenheit, all-year-round. This temperature may not sound like a lot, but it can be used to cool or heat homes and offices with the help of special pipes called loops. A heat exchanger and electric compressor are required to pull heat from the pipes to the duct system of the building. During summer, the process is reversed.
- Direct geothermal energy. When asked “Where is geothermal energy used?” many people respond hot springs and public baths. This answer is correct, but it refers only to direct geothermal energy. In areas where geothermal reservoirs touch the Earth’s surfaces, hot water and steam can be piped to directly heat homes or public spaces. Once used, water is injected back into the reservoir.
For more specific information on how and where geothermal energy is used, please check our ‘Examples of Geothermal Energy’ section below.
7. What is the Environmental Impact of Geothermal Energy?
In the case of Geothermal Power and geothermal heat pumps, environmental impact is minimal. For geothermal power plants it’s a different story. Although emissions in comparison to fossil fuel powered plants are slim to none, some risks exist.

The environmental impacts in the case of hydrothermal plants (the most developed type of geothermal plants) differ according to cooling and conversion technology used. There are 4 major types of environmental impacts of geothermal plants:
- Air Emissions. When discussing air emissions we have to make a clear distinction between open-loop (gases removed from the well are released into the atmosphere) and closed-loop (gases removed from the well are reinjected into the soil) systems. Closed-loop system emissions are minimal, while open-loop systems may have negative environmental impacts (releasing boron, methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide into the atmosphere). Some hydrothermal plants can also produce mercury emissions, which must immediately be mitigated with mercury filters.
- Life-cycle Global Warming Emissions. Enhanced geothermal systems have life-cycle global warning emission of roughly 0.2 pounds CO2 per KWH. Life-cycle global warning emission oscillates between 0.6 and 2 pounds of CO2 per KWH for natural gas generated electricity, and between 1.4 and 3.6 pounds CO2 per KWH for coal-generated electricity.
- Water Technology & Use. Geothermal energy plants can affect the consumption and quality of water. Underground hot water is rich in salt, sulfur and other minerals. Because most power plants are closed-loop, the water returns to the reservoir. There have been no reported cases of water contamination in U.S. geothermal plants.
Water in geothermal plants is also used for re-injection (some water is lost when it turns into steam) and cooling. In order to maintain a constant stream of water in the plant, outside water must be injected. Non-potable treated wastewater can be used to reduce environmental impact. As far as cooling is concerned, U.S. plants can use either freshwater or geothermal fluid. Using the latter will significantly reduce overall water impact.
- Land Use varies according to the size of the geothermal plant, the type of energy conversion system, power capacity, piping systems, arrangement of wells and auxiliary buildings. The largest geothermal plant stretches over 78 square kilometers. Because water is removed from the Earth’s surface, a phenomenon called ‘land subsidence’ may occur (the land surface sinks). Most geothermal plants address this issue by reinjecting waste water into the underground reservoir. Lastly, it has been demonstrated that placing hydrothermal plants on geological ‘hot spots’ will increase the risk of small earthquakes. This problem can be avoided by building plants at an appropriate distance from fault lines.
Geothermal Energy Pros and Cons
Geothermal Power is a great alternative to fossil fuels. However, every type of renewable resource has certain drawbacks. Let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy to understand whether or not it is a suitable choice for your house or business.
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
The benefits of geothermal energy are many:
- Environment-friendly. Geothermal power is environment friendly in almost all aspects of production and use. As a matter of fact, studies show that it is the power source with the lowest impact on the environment.
- Abundant supply. Geothermal energy is not subject to the same problems that wind and solar power have. There is practically an infinite supply of geothermal resource in the Earth’s core. Because geothermal energy is intrinsically basic and dependable, you will never have to worry about it running out.
- Cost-effective. Most homeowners use Geothermal Power for cooling and heating purposes because it is cheaper. Although the initial investment is high, geothermal energy can result in 25-50% savings on cooling and 30-60% savings on heating. These savings will cover the initial cost over the years.
- Small Land Footprint. Geothermal Power requires a substantial amount of underground piping. However, this does not affect land footprint. This form of renewable energy has the smallest land footprint of all renewable energies in the world.
- No fossil fuels needed. Geothermal energy requires no transportation or mining. The entire process happens with the help of the Earth’s heat and water. This means that there won’t be any gas or fume emissions.
- Without a doubt, the most important benefit of Geothermal Power is the fact that it’s renewable. Heat extracted from the Earth’s core will be available as long as the Planet exists. Water will also be available as long as the natural cycle continues to occur. On the other hand, fossil fuels have an expiration date.
- Innovation in technology.
- Other benefits: The production process of G.E. can scrub out sulfur that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. Most areas in the world, especially those close to the ‘Ring of Fire’ have access to geothermal energy. New technologies will be able to utilize lower temperatures. G.E. can be used in new constructions as well as retrofit situations.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is definitely not bad for the environment. It is actually far from bad, but there are several drawbacks that you need to take into account before venturing into the unclear waters of sustainable energy sources. Here are some of the most important geothermal energy disadvantages:
- It’s very expensive. I’m not going to lie to you, the upfront cost of Geothermal Power is crazy high. This has proven to be a huge setback for many home-owners. The geo thermal energy cost for an average-sized house can hover between $10,000 and $20,000.
- Suitable destinations are far from urban areas. Everything that has to deal with G.E. is usually far, far away from any sign of civilization. Although geothermal sources are widely spread, the prime destinations are extremely zone specific.
- Risk of Earthquakes. As mentioned above, geothermic energy can lead to surface instability. Hydraulic fracturing, which is necessary for building large geothermal power plans, can trigger small earthquakes.
- Some environment concerns. Despite the fact that G.E. is mostly environmentally friendly, there are certain concerns regarding water use for large-scale plants. In addition to this, there are several compounds that go into the ground, water and air during the production process.
- May run out of steam. If the heat is not properly taken care of, the plant can run out of steam and cause a meltdown.
- High temperatures are an absolute must. If the area in question doesn’t reach at least 350 degrees Fahrenheit it may be difficult for processes to occur as you wish them to.
After listing the pros and cons of geothermal energy, it becomes clear that the advantages clearly outweigh the disadvantages.
Cost of Geothermal Energy
There’s no need to sugarcoat it. The upfront cost for Geothermal Power is terrifying. Depending on location, configuration, site accessibility or the amount of drilling and digging required, the cost of installing G.E. systems in an existing house can reach $30,000. In addition to this, the existing system may also require ductwork modifications and large-scale excavations – meaning more money you have to take out of your pocket.
Even if you install geothermal energy systems in a new home, the costs will be at least 40% more than that of a traditional HVAC system.
The good news is that upfront costs can be recuperated within 4-15 years, depending on the cost of installation and utility rates. You will have to conduct extensive research to understand whether or not geothermal systems make sense in your situation.
Interesting Geothermal Energy Facts

Types of Geothermal Energy
Below are 12 mind-boggling, interesting and fun facts about geothermal energy:
- Today’s Geothermal Energy: There are four kinds of geothermal resources: hot dry rock, magma, geo-pressured and hydrothermal. We only use the latter, as the first three are only in infant stages of development.
- There are numerous geothermal ‘suitable areas’ scattered across the globe.
- G.E. supplies less than 1% of the United States’ electricity. However, it supplies 18% of Iceland’s total electricity.
- Geothermal Power has extremely low emission of greenhouse gases – approximately 3% of CO2 emissions of fossil fuel power stations.
- G.E. is capable of producing 10% of U.S. electricity by 2050.
- The only real problem of geothermal energy is lack of accessible sites.
- As of 2014, 24 countries use geothermal energy to produce electricity. 70 countries use it for other forms of heating.
- The oldest bath fed from a hot spring is believed to be China’s Lisan Mountain. The stone pool was made in the 3rd century B.C.
- IKEA has embraced G.E. in order to reduce carbon footprint & cut-down costs. Denver IKEA is the first IKEA store in the U.S. to be built with geothermal technology.
- According to Scientific America, the earliest forms of life might have evolved in geothermal pools and hot-spots, like those at Yellowstone, not in the Sea. Yellowstone’s ‘Morning Glory Pool’ is teeming with bacteria and life-forms that are rich in potassium, zinc and phosphorus – the matter of life.

- The most popular geothermal system is Yellowstone National Park. Over 200 geysers erupt in the park every year. Old Faithful, Yellowstone’s largest geyser, can shoot 14,000-32,000 liters of hot, boiling water to a height of 32-56 meters.
- Google is also interested in geothermal energy. The company funded Southern Methodist University’s research to explore new ways in which geothermal can be used with today’s technology.
Examples of Geothermal Energy
One of the best ways to explain geothermal energy for kids, especially now that this sustainable technology is being implemented in schools across the United States (e.g. Table Mound Elementary School, Dubuque, Iowa), is to share examples and case-studies. Below is a list of G.E. examples that will help put things into perspective:
1. Geothermal Potential in Alaska
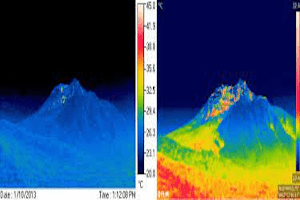
Alaska is situated on the Ring of Fire, the volcanic arc circling the Pacific Ocean, which means that it is a perfect place for geothermal development. Scientific studies show that there are more than 100 thermal springs and wells in Alaska, as well as more than 130 volcanoes & volcanic fields that have been active in the last 2 million years, and over 50 that have been active in the last 230 years. In light of this information, the USGS identified four major areas that would benefit from further geothermal energy study:
- Edgecumbe on Kruzof Island
- The Ring of Fire Volcanoes on the Aleutian Chain (Alaska Peninsula).
- The Hot Springs situated north-east of Ketchikan.
- The Hot Springs that run east-west from the Yukon Territory (Canadian land) to the Seward Peninsula.

Many members of the Alaskan community are considering the uses of geothermal energy for the production of electricity, but scientists believe they could find better value in direct heat. As you can imagine, the heating costs for homes in Alaska are very high. G.E. could provide an environmentally safe and reliable alternative. The only real drawback to geothermal power in this area represents the remote locations for many geothermal hot spots.
A great example of geothermal hot-spot used for direct heat is the Chena Hot Springs Resort, which facilitates heat and power to its buildings, greenhouses and swimming pools. This resort is capable of producing 680 KW that run on 165 degree Fahrenheit water (lowest possible temperature for G.E. plants).

The resort, which was built with an initial budget of $2.1 million, also demonstrates the applications of geothermal energy for refrigeration (its 16-ton absorption chiller kept an ice museum cool all-year-round).
2. Geothermal Energy for Homes
Residential G.E. solutions are slowly gaining popularity. The concept of geothermal energy homes is quite simple: during summer, heat from the home is sent underground through a framework of pipes, where it naturally cools. During winter, heat from the earth flows through the pipes and into the home.
Examples of Geothermal Energy Home Projects:

3. Uses of Geothermal Energy in Farming
A common use of geothermal energy is to heat greenhouses. In Tuscany, Italy, farmers use geothermal water to heat vegetables during winter. As a matter of fact, 80% of energy demand for vegetable growers is met with the help of geothermal energy. This renewable form of energy is also used to in fish farms, where farmers grow shellfish, tropical fish, catfish and alligators.
4. Industrial Uses of Geothermal Energy
Various industrial sectors use geothermal energy to dry wood, wool, or fruits and to extract gold and silver from ore. Below is a graphic representation of the industrial uses of geothermal energy for different temperatures.

Other Examples of Geothermal Energy:
- Puna Geothermal Venture (PGV): PGV represents a geothermal energy conversion plant that brings hot liquid and steam from below the earth to produce electricity. The electricity produced by this plant has a contract capacity of 30 megawatts with an 8 megawatt expansion.
Future of Geothermal Energy
The future of G.E. can be summed up in a single word: more. The heat formed deep inside the Earth’s surface can now be collected, harnessed and used to shape a better future for the next generations. At the moment, G.E. is considered the third most important type of renewable energy after solar and wind.
As humankind starts to move more towards renewable energy sources and continues to evaluate sustainable alternatives for power and heat generation, G.E. will become even more important. Assuming that the technology used for G.E. will also improve (and it will), the high upfront costs of geothermal systems will also decrease over-time, making it accessible to the masses.
“Geothermal energy has significant base-load potential, requires no storage, and, thus, it complements other renewables – solar (CSP and PV), wind, hydropower – in a lower-carbon energy future.” – Source: The Future of G.E., Massachusetts Institute of Technology
For more information on the future of Geothermal Energy please read the ‘Impact of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) on the United States in the 21st Century’ study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
For more information on G.E. we recommend becoming familiar with the materials published on the Geothermal Energy Association website.
Geothermal Energy Pictures
Before we conclude this extensive guide, let’s take a look at several G.E. images that will give you a truer description of the benefits of this renewable source with high energy efficiency:

Energy Renewable Power Plant in Nesjavellir, Iceland

Geothermal Energy Diagram for Kids

Krafla Geothermal Power Station

Geothermal Energy for Sustainable Homes
Image Sources: 1, 2.1., 2.2., 2.3., 3, 3.1., 4.1., 4.2., 4.3., 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15.



























































































































































































































































































































it’s really effective …