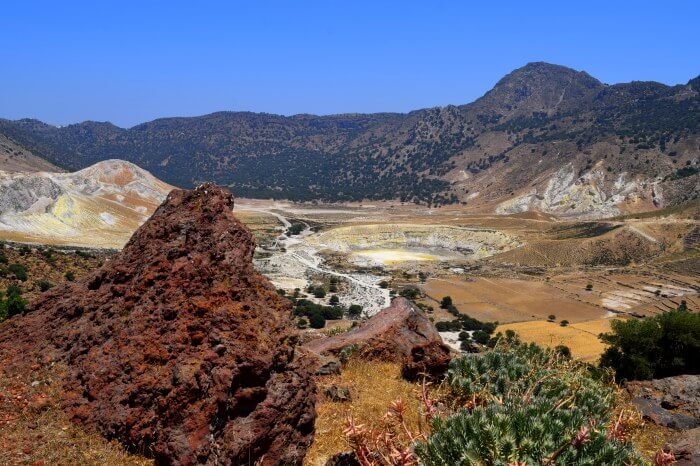
Intra-caldera deposits (1,2)
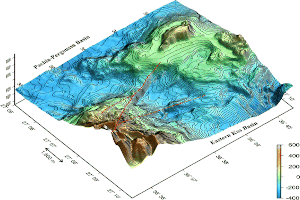
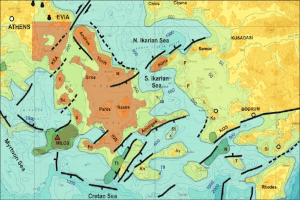
These are fine, mainly clay materials deposited on the eastern half of the caldera depression creating the plane of Lakki. Maximum thickness values are as high as 50-60m.
These resulted from erosion of the caldera cliffs, weathering of volcanites, which is especially severe due to the fumarolic activity, as well as mud flows ejecting during the multiple hydrothermal explosions.
Moreover, lacustrine sediment layers are found, containing diatomites and clay with carbonized vegetation.
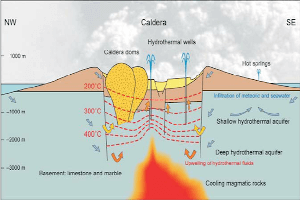
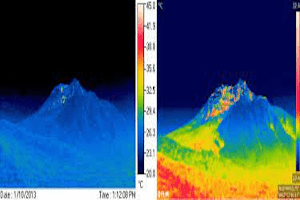
The floor of the caldera hosts traces of 20 hydrothermal craters (Marini et al, 1993, Vougioukalakis, 1998). Ten of them are preserved in very good condition. Hydrothermal explosions have been recorded in 1871-73 (Gorceix 1873, 1874) and 1887 (Martelli, 1917).