Scientific classification
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Angiosperms |
| Class: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Asphodelaceae |
| Subfamily: | Asphodeloideae |
| Genus: | Asphodelus |
| Species: | A. aestivus |
Binomial name
Asphodelus aestivus
Brot.
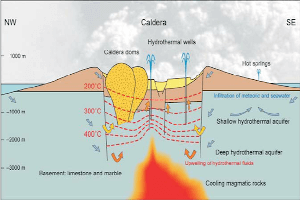
Asphodelus aestivus, the summer asphodel, is a species of asphodel, a common Western Mediterranean geophyte with a short vertical rhizome and basal leaves. Its flowers are actinomorphic, pinkish-white, with six perianth segments, 14–19 mm long and six stamens of the same length, in two whorls. Its distribution is limited to the Western Mediterranean, mainly found in Portugal and Spain on the European mainland.[2] There has been a lot of confusion over the nomenclature and taxonomy of the species, owing to its similarity to Asphodelus ramosus.[3][4] It grows in dry grasslands, phrygana and on rocky or sandy ground.[1]
Physical characteristics
The Asphodelus aestivus is a geophyte, having an underground storage organ which enables the plant to survive adverse conditions, such as excessive heat and drought. Its leaves, growing to a height of 60 centimetres (24 in)–80 centimetres (31 in), contain alkaloids that are harmful to sheep and goats in the wet, winter months, but during the summer when their leaves dry out, they lose their toxicity.[5][6] In the Iberian Peninsula it flowers from June to September, although in the Algarve (SW Portugal) it may flower in May or at the end of April. There, the leaves are already withered by the time the plants flower.[7]
Asphodelus ramosus, also known as branched asphodel, is a perennial herb in the Asparagales order. Similar in appearance to Asphodelus albus and particularly Asphodelus cerasiferus, it may be distinguished by its highly branched stem and smaller fruits.[1][2]
Asphodelus ramosus is native to the Mediterranean region of southern Europe, northern Africa, and the Middle East. It can also be found in the Canary Islands.[3][4][5] It is particularly common on the Catalan coast, where it shows an affinity for acidic soils, mainly schist. It is to be found close to the sea on the slopes of the Albères massif, where it forms abundant colonies in April to May. Its very numerous flowers are white with six tepals bearing a central brown streak. The fruits are small round capsules.[6]
It has been thought to be Homer’s asphodel of the underworld,[7] but so has the closely related Asphodeline lutea.
Asphodel is known to contain colchicine, a chemical used in the treatment of gout.[citation needed] It was mentioned by Dioscorides, amongst others, for this purpose.[8]
Uses
Some traditional folk usages of the plant have been to make a glue from the plant’s root. A remedy against warts is also derived from its root.[6] According to Dioscorides, a concoction made from its roots (mixed with wine) induces vomiting.[8] Formerly, the entire plant was used in treating poisonous snake bites (its efficacy yet to be proven scientifically).
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia